EIT week39-1 Electroluminescent Displays
EIT week39-1 Electroluminescent Displays
Electroluminescent Displays
Overview
- Course: Engineering Interaction Technologies
- Professor: Michael Wessely, Interactive Matter Lab
Key Concepts of Electroluminescent (EL) Displays
- Definition: Electroluminescent displays use a material that emits light in response to an electric current or a strong electric field.
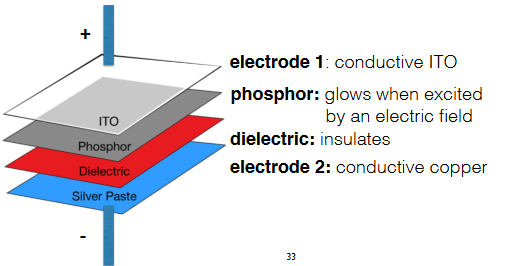
- Components:
- Electrode 1: Conductive Indium Tin Oxide (ITO)
- Phosphor Layer: Glows when excited by an electric field
- Dielectric Layer: Insulates the electrodes to prevent short-circuits
- Electrode 2: Conductive copper
Fabrication Techniques
- Lab 9 Focus: Spraying of EL displays, highlighting methods to apply layers and shape the phosphor for custom designs.
- Material Handling: Techniques for shaping ITO or copper layers to determine the glowing areas of the display.
Types of EL Displays
- Area Display: Basic type where large areas glow to form a uniform backlight or specific shapes.
- Segment Display: Composed of multiple smaller, individually controlled areas for creating numbers or simple icons.
- Matrix Display: Offers the highest control over shapes by allowing individual control of small segments in a grid, facilitating complex imagery or text.
Advanced EL Display Features
- Rollable and Stretchable Displays: New technologies enabling EL displays to be applied on flexible surfaces that can be bent or stretched.
- Touch Input Integration: Using capacitive sensing to allow EL displays to detect touch inputs, making them interactive. Techniques include multiplexing to alternate between display and touch sensing without user detection.
Interactive Features
- Smart Integration: Incorporates capacitive touch sensing directly into the display, which allows for interactive applications, adjusting content dynamically based on user interaction.
Challenges and Innovations
- Customization Challenges: How to effectively customize the shape and functionality of EL materials using techniques like spraying.
- Potential Innovations: Exploring roll-to-roll processes and other industrial techniques to streamline production and enhance the functional integration of EL displays.
Educational Insights
- Practical Sessions: Hands-on labs that involve creating and manipulating EL displays to understand their properties and applications better.
- Discussion Points: Debates on the feasibility and effectiveness of current EL technology in real-world applications, touching on aspects like durability, energy efficiency, and integration complexity.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.